 |
| Corn with fungal infection (Image © Biomin) |
A regional mycotoxin survey was conducted with 162 corn samples that were analysed from the harvest of 2013 and 2014 from the provinces of Anhui (5), Hebei (15), Henan (14), Heilongjiang (32), Hubei (9), Jiangsu (2), Jilin (19), Liaoning (31), Neimenggu (8), Shandong (9), Shanxi and Shaanxi (18).
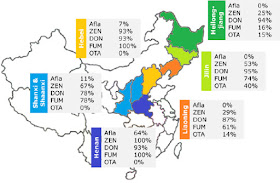 |
| Figure 1: Provinces in focus: prevalence of mycotoxins as a percentage of total samples analysed in each region (>10 samples) |
- 94 percent of all corn samples from China were contaminated and almost three quarters contained two or more mycotoxins
- The most frequent mycotoxin was deoxynivalenol with 90 percent of positive samples and an average of 488 ppb
- Fumonisins was detected in more than two thirds of all Chinese corn samples at an average of 1425 ppb, a level that poses a health threat to swine which is one of the most sensitive species towards this toxin
- More than half of all corn samples were contaminated with the mycoestrogen zearalenone at an average of 108 ppb
 |
| Table 1: Mycotoxin occurrence in Chinese corn samples in 2014 |
- In Hebei, all corn samples surveyed were contaminated with FUM at a high average of 2555 ppb. Also ZEN and DON (93 percent) were present at a high prevalence
- More than ¾ of all corn samples from Shanxi and Shaanxi were contaminated with DON and FUM at average levels of 819 ppb and 1477 ppb, respectively
- As predicted, Henan was the region most affected by mycotoxin contamination: FUM and ZEN were detected in all corn samples at the highest average values observed (4564 ppb and 254 ppb, respectively), DON was present in 93 percent of the samples at a high 850 ppb and also the highest prevalence and average of Afla (64 percent and 21 ppb) were recorded in this province
- The highest threat in the Northeast provinces of Heilongjang, Jilin and Liaoning was posed by DON as 94 percent, 95 percent and 87 percent of corn samples were contaminated, respectively. Also FUM was detected in more than 2/3 of samples from Jilin and Liaoning
Visit the mycotoxins.info site HERE.
The Global Miller
This blog is maintained by The Global Miller staff and is supported by the magazine GFMT
which is published by Perendale Publishers Limited.
For additional daily news from milling around the world: global-milling.com

No comments:
Post a Comment